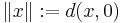Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric or distance function is a function which defines a distance between elements of a set. A set with a metric is called a metric space. A metric induces a topology on a set but not all topologies can be generated by a metric. When a topological space has a topology that can be described by a metric, we say that the topological space is metrizable.
In differential geometry, the word "metric" is also used to refer to a structure defined only on a differentiable manifold which is more properly termed a metric tensor (or Riemannian or pseudo-Riemannian metric).
Contents |
Definition
A metric on a set X is a function (called the distance function or simply distance)
d : X × X → R
(where R is the set of real numbers). For all x, y, z in X, this function is required to satisfy the following conditions:
- d(x, y) ≥ 0 (non-negativity)
- d(x, y) = 0 if and only if x = y (identity of indiscernibles. Note that condition 1 and 2 together produce positive definiteness)
- d(x, y) = d(y, x) (symmetry)
- d(x, z) ≤ d(x, y) + d(y, z) (subadditivity / triangle inequality).
The first condition is implied by the others.
A metric is called an ultrametric if it satisfies the following stronger version of the triangle inequality where points can never fall 'between' other points:
- For all x, y, z in M, d(x, z) ≤ max(d(x, y), d(y, z))
A metric d on X is called intrinsic if any two points x and y in X can be joined by a curve with length arbitrarily close to d(x, y).
For sets on which an addition + : X × X → X is defined, d is called a translation invariant metric if
- d(x, y) = d(x + a, y + a)
for all x, y and a in X.
Notes
These conditions express intuitive notions about the concept of distance. For example, that the distance between distinct points is positive and the distance from x to y is the same as the distance from y to x. The triangle inequality means that the distance from x to z via y is at least as great as from x to z directly. Euclid in his work stated that the shortest distance between two points is a line; that was the triangle inequality for his geometry.
If a modification of the triangle inequality
- 4*. d(x, z) ≤ d(z, y) + d(y, x)
is used in the definition then property 1 follows straight from property 4*. Properties 2 and 4* give property 3 which in turn gives property 4.
Examples
- The discrete metric: if x = y then d(x,y) = 0. Otherwise, d(x,y) = 1.
- The Euclidean metric is translation and rotation invariant.
- The taxicab metric is translation invariant.
- More generally, any metric induced by a norm is translation invariant.
- If
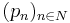 is a sequence of seminorms defining a (locally convex) topological vector space E, then
is a sequence of seminorms defining a (locally convex) topological vector space E, then
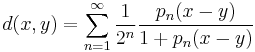
- is a metric defining the same topology. (One can replace
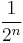 by any summable sequence
by any summable sequence 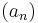 of strictly positive numbers.)
of strictly positive numbers.)
- Graph metric, a metric defined in terms of distances in a certain graph.
- The Hamming distance in coding theory.
- The Fubini–Study metric on complex projective space.
Equivalence of metrics
For a given set X, two metrics d1 and d2 are called topologically equivalent (uniformly equivalent) if the identity mapping
- id: (X,d1) → (X,d2)
is a homeomorphism (uniform isomorphism).
For example, if 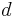 is a metric, then
is a metric, then 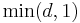 and
and 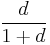 are metrics equivalent to
are metrics equivalent to 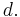
See also notions of metric space equivalence.
Metrics on vector spaces
Norms on vector spaces are equivalent to certain metrics, namely homogeneous, translation-invariant ones. In other words, every norm determines a metric, and some metrics determine a norm.
Given a normed vector space 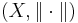 we can define a metric on X by
we can define a metric on X by
 .
.
The metric d is said to be induced by the norm  .
.
Conversely if a metric d on a vector space X satisfies the properties
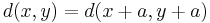 (translation invariance)
(translation invariance) (homogeneity)
(homogeneity)
then we can define a norm on X by
Similarly, a seminorm induces a pseudometric (see below), and a homogeneous, translation invariant pseudometric induces a seminorm.
Generalized metrics
There are numerous ways of relaxing the axioms of metrics, giving rise to various notions of generalized metric spaces. These generalizations can also be combined. The terminology used to describe them is not completely standardized. Most notably, in functional analysis pseudometrics often come from seminorms on vector spaces, and so it is natural to call them "semimetrics". This conflicts with the use of the term in topology.
Extended metrics
Some authors allow the distance function d to attain the value ∞, i.e. distances are non-negative numbers on the extended real number line. Such a function is called an extended metric. Every extended metric can be transformed to a finite metric such that the metric spaces are equivalent as far as notions of topology (such as continuity or convergence) are concerned. This can be done using a subadditive monotically increasing bounded function which is zero at zero, e.g. d′(x, y) = d(x, y) / (1 + d(x, y)) or d′′(x, y) = min(1, d(x, y))).
The requirement that the metric take values in [0,∞) can even be relaxed to consider metrics with values in other directed sets. The reformulation of the axioms in this case leads to the construction of uniform spaces: topological spaces with an abstract structure enabling one to compare the local topologies of different points.
Pseudometrics
A pseudometric on X is a function d : X × X → R which satisfies the axioms for a metric, except that instead of the second (identity of indiscernibles) only d(x,x)=0 for all x is required. In other words, the axioms for a pseudometric are:
- d(x, y) ≥ 0
- d(x, x) = 0 (but possibly
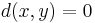 for some distinct values
for some distinct values 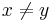 .)
.) - d(x, y) = d(y, x)
- d(x, z) ≤ d(x, y) + d(y, z).
This is the most common generalization of metrics. In some contexts, pseudometrics are referred to as semimetrics because of their relation to seminorms.
Quasimetrics
Occasionally, a quasimetric is defined as a function that satisfies all axioms for a metric with the possible exception of symmetry:[1]
- d(x, y) ≥ 0
- d(x, y) = 0 if and only if x = y
- (dropped)
- d(x, z) ≤ d(x, y) + d(y, z).
If d is a quasimetric on X, a metric d' on X can be formed by taking
- d'(x, y) = 1⁄2(d(x, y) + d(y, x)).
Quasimetrics are common in real life. For example, given a set X of mountain villages, the typical walking times between elements of X form a quasimetric because travel up hill takes longer than travel down hill. Another example is a taxicab geometry topology having one-way streets, where a path from point A to point B comprises a different set of streets than a path from B to A. Nevertheless, this notion is rarely used in mathematics, and its name is not entirely standardized.[2]
A quasimetric on the reals can be defined by setting
- d(x, y) = y − x if y ≥ x, and
- d(x, y) = 1 otherwise.
The topological space underlying this quasimetric space is the Sorgenfrey line.
Semimetrics
A semimetric on X is a function d : X × X → R that satisfies the first three axioms, but not necessarily the triangle inequality:
- d(x, y) ≥ 0
- d(x, y) = 0 if and only if x = y
- d(x, y) = d(y, x)
Some authors work with a weaker form of the triangle inequality, such as:
- d(x, z) ≤ ρ (d(x, y) + d(y, z)) (ρ-relaxed triangle inequality)
- d(x, z) ≤ ρ max(d(x, y), d(y, z)) (ρ-inframetric inequality).
The ρ-inframetric inequality implies the ρ-relaxed triangle inequality (assuming the first axiom), and the ρ-relaxed triangle inequality implies the 2ρ-inframetric inequality. Semimetrics satisfying these equivalent conditions have sometimes been referred to as "quasimetrics"[3], "nearmetrics"[4] or inframetrics.[5]
The ρ-inframetric inequalities were introduced to model round-trip delay times in the internet.[5] The triangle inequality implies the 2-inframetric inequality, and the ultrametric inequality is exactly the 1-inframetric inequality.
Premetrics
Relaxing the last three axioms leads to the notion of a premetric, i.e. a function satisfying the following conditions:
- d(x, y) ≥ 0
- d(x, x) = 0
This is not a standard term. Sometimes it is used to refer to other generalizations of metrics such as pseudosemimetrics[6] or pseudometrics[7]; in translations of Russian books it sometimes appears as "prametric"[8].
Any premetric gives rise to a topology as follows. For a positive real r, the open r-ball centred at a point p is defined as
- Br(p) = { x | d(x, p) < r }.
A set is open if for any point p in the set there is an r-ball centred at p which is contained in the set. In general, the open r-balls themselves need not be open sets with respect to this topology. In fact, the interior of an r-ball may be empty. Thus every premetric space is a topological space, and in fact a sequential space.
As for metrics, the distance between two sets A and B, is defined as
- d(A, B) = infx∊A, y∊B d(x, y).
This defines a premetric on the power set of a premetric space. If we start with a (pseudosemi-)metric space, we get a pseudosemimetric, i.e. a symmetric premetric. Any premetric gives rise to a preclosure operator cl as follows:
- cl(A) = { x | d(x, A) = 0 }.
Pseudoquasimetrics
The presyllables pseudo-, quasi- and semi- can also be combined, e.g., a pseudoquasimetric (sometimes called called hemimetric) relaxes both the indiscernibility axiom and the symmetry axiom and is simply a premetric satisfying the triangle inequality. For pseudoquasimetric spaces the open r-balls form a basis of open sets. A very basic example of a pseudoquasimetric space is the set {0,1} with the premetric given by d(0,1) = 1 and d(1,0) = 0. The associated topological space is the Sierpiński space.
Sets equipped with an extended pseudoquasimetric were studied by William Lawvere as "generalized metric spaces".[9][10] From a categorical point of view, the extended pseudometric spaces and the extended pseudoquasimetric spaces, along with their corresponding nonexpansive maps, are the best behaved of the metric space categories. One can take arbitrary products and coproducts and form quotient objects within the given category. If one drops "extended", one can only take finite products and coproducts. If one drops "pseudo", one cannot take quotients. Approach spaces are a generalization of metric spaces that maintains these good categorical properties.
Important cases of generalized metrics
In differential geometry, one considers metric tensors, which can be thought of as "infinitesimal" metric functions. They are defined as inner products on the tangent space with an appropriate differentiability requirement. While these are not metric functions as defined in this article, they induce metric functions by integration. A manifold with a metric tensor is called a Riemannian manifold. If one drops the positive definiteness requirement of inner product spaces, then one obtains a pseudo-Riemannian metric tensor, which integrates to a pseudo-semimetric. These are used in the geometric study of the theory of relativity, where the tensor is also called the "invariant distance".
See also
- Acoustic metric
- Complete metric
Notes
- ↑ E.g. Steen & Seebach (1995).
- ↑ Rolewicz, Stefan (1987), Functional Analysis and Control Theory: Linear Systems, Springer, ISBN 9027721866, OCLC 13064804 This book calls them "semimetrics", which is unfortunate because the same term is frequently used for two other generalizations of metrics.
- ↑ Xia, Q. (2009), "The Geodesic Problem in Quasimetric Spaces", Journal of Geometric Analysis 19: 452–479, doi:10.1007/s12220-008-9065-4
- ↑ Qinglan Xia (2008). "The geodesic problem in nearmetric spaces". arΧiv:0807.3377 [math.MG].
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 * Fraigniaud, P.; Lebhar, E.; Viennot, L. (2008), "The inframetric model for the internet", IEEE INFOCOM 2008. the 27th Conference on Computer Communications: 1085–1093, doi:10.1109/INFOCOM.2008.163, http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.113.6748, retrieved 2009-04-17.
- ↑ Buldygin, V.V.; Kozachenko, I.U.V. (2000), Metric characterization of random variables and random processes.
- ↑ Khelemskiĭ (2006), Lectures and exercises on functional analysis.
- ↑ Arkhangel'skii & Pontryagin (1990). Aldrovandi, R.; Pereira, J.G. (1995), An introduction to geometrical physics.
- ↑ Lawvere, F.W. (2002) [1973], Metric spaces, generalised logic, and closed categories, Reprints in Theory and Applications of Categories, 1, pp. 1–37.
- ↑ Vickers, Steven (2005), "Localic completion of generalized metric spaces I", Theory and Applications of Categories 14: 328–356, http://www.tac.mta.ca/tac/volumes/14/15/14-15abs.html
References
- Arkhangel'skii, A.V.; Pontryagin, L.S. (1990), General Topology I: Basic Concepts and Constructions Dimension Theory, Encyclopaedia of Mathematical Sciences, Springer, ISBN 3-540-18178-4
- Steen, Lynn Arthur; Seebach, J. Arthur Jr. (1995) [1978], Counterexamples in Topology, Dover, MR507446, ISBN 978-0-486-68735-3, OCLC 32311847
- Quasimetric space on PlanetMath
- Semimetric on PlanetMath